1
| 位于CPU与主存之间的高速缓冲存储器(Cache)用于存放部分主存数据的拷贝, 主存地址与Cache地址之间的转换工作由(1)完成。 |
| A. 硬件 |
| B. 软件 |
| C. 用户 |
| D. 程序员 |
2
| 内存单元按字节编址,地址0000A000H〜0000BFFFH共有(2)个存储单元。 |
| A. 8192K |
| B. 1024K |
| C. 13K |
| D. 8K |
3
| 相联存储器按(3)访问。 |
| A. 地址 |
| B. 先入后出的方式 |
| C. 内容 |
| D. 先入先出的方式 |
4
| 若CPU要执行的指令为:MOV R1, #45 (即将数值45传送到寄存器R1中),则该指令中采用的寻址方式为(4)。 |
| A. 直接寻址和立即寻址 |
| B. 寄存器寻址和立即寻址 |
| C. 相对寻址和直接寻址 |
| D. 寄存器间接寻址和直接寻址 |
5
| 数据流图(DFD)对系统的功能和功能之间的数据流进行建模,其中顶层数据流图描述了系统的(5)。 |
| A. 处理过程 |
| B. 输入与输出 |
| C. 数据存储 |
| D. 数据实体 |
6
| 以下关于类继承的说法中,错误的是(6) 。 |
| A. 通过类继承,在程序中可以复用基类的代码 |
| B. 在继承类中可以增加新代码 |
| C. 在继承类中不能定义与被继承类(基类)中的方法同名的方法 |
| D. 在继承类中可以覆盖被继承类(基类)中的方法 |
7
下图是一个软件项目的活动图,其中顶点表示项目里程碑,连接顶点的边表示活动, 边上的值表示完成活动所需要的时间,则(7)在关键路径上。 |
| A. B |
| B. C |
| C. D |
| D. H |
8
| 软件开发的增量模型(8)。 |
| A. 最适用于需求被清晰定义的情况 |
| B. 是一种能够快速构造可运行产品的好方法 |
| C. 最适合于大规模团队开发的项目 |
| D. 是一种不适用于商业产品的创新模型 |
9
| 假设某软件公司与客户签订合同开发一个软件系统,系统的功能有较清晰的定义, 且客户对交付时间有严格要求,则该系统的开发最适宜采用(9)。 |
| A. 瀑布模型 |
| B. 原型模型 |
| C. V模型 |
| D. 螺旋模型 |
10
| 中国企业M与美国公司L进行技术合作,合同约定M使用一项在有效期内的美国专利,但该项美国专利未在中国和其他国家提出申请。对于M销售依照该专利生产的产品,以下叙述正确的是 (10) 。 |
| A. 在中国销售,M需要向L支付专利许可使用费 |
| B. 返销美国,M不需要向L支付专利许可使用费 |
| C. 在其他国家销售,M需要向L支付专利许可使用费 |
| D. 在中国销售,M不需要向L支付专利许可使用费 |
11
| 网络中存在各种交换设备,下面的说法中错误的是(11)。 |
| A. 以太网交换机根据MAC地址进行交换 |
| B. 帧中继交换机只能根据虚电路号DLCI进行交换 |
| C. 三层交换机只能根据第三层协议进行交换 |
| D. ATM交换机根据虚电路标识进行信元交换 |
12
| 通过以太网交换机连接的一组工作站(12)。 |
| A. 组成一个冲突域,但不是一个广播域 |
| B. 组成一个广播域,但不是一个冲突域 |
| C. 既是一个冲突域,又是一个广播域 |
| D. 既不是冲突域,也不是广播域 |
13
| E1载波的数据速率是(13) Mb/s, T1载波的数据速率是(14) Mb/s。 |
| A. 1.544 |
| B. 2.048 |
| C. 6.312 |
| D. 8.448 |
14
| E1载波的数据速率是(13) Mb/s, T1载波的数据速率是(14) Mb/s。 |
| A. 1.544 |
| B. 2.048 |
| C. 6.312 |
| D. 8.448 |
15
| 设信道带宽为3400Hz,采用PCM编码,采样周期为125us,每个样本量化为256个等级,则信道的数据速率为(15)。 |
| A. 10Kb/s |
| B. 16Kb/s |
| C. 56Kb/s |
| D. 64Kb/s |
16
| 曼彻斯特编码的效率是(16) %, 4B/5B编码的效率是(17) %。 |
| A. 40 |
| B. 50 |
| C. 80 |
| D. 100 |
17
| 曼彻斯特编码的效率是(16) %, 4B/5B编码的效率是(17) %。 |
| A. 40 |
| B. 50 |
| C. 80 |
| D. 100 |
18
| ARP协议的作用是(18),它的协议数据单元封装在(19)中传送。ARP请求是采用(20)方式发送的。 |
| A. 由MAC地址求IP地址 |
| B. 由IP地址求MAC地址 |
| C. 由IP地址查域名 |
| D. 由域名查IP地址 |
19
| ARP协议的作用是(18),它的协议数据单元封装在(19)中传送。ARP请求是采用(20)方式发送的。 |
| A. IP分组 |
| B. 以太帧 |
| C. TCP段 |
| D. UDP报文 |
20
| ARP协议的作用是(18),它的协议数据单元封装在(19)中传送。ARP请求是采用(20)方式发送的。 |
| A. 单播 |
| B. 组播 |
| C. 广播 |
| D. 点播 |
21
| RIP是一种基于(21)算法的路由协议,一个通路上最大跳数是(22),更新路由表的原则是到各个目标网络的(23)。 |
| A. 链路状态 |
| B. 距离矢量 |
| C. 固定路由 |
| D. 集中式路由 |
22
| RIP是一种基于(21)算法的路由协议,一个通路上最大跳数是(22),更新路由表的原则是到各个目标网络的(23)。 |
| A. 7 |
| B. 15 |
| C. 31 |
| D. 255 |
23
| RIP是一种基于(21)算法的路由协议,一个通路上最大跳数是(22),更新路由表的原则是到各个目标网络的(23)。 |
| A. 距离最短 |
| B. 时延最小 |
| C. 流量最小 |
| D. 路径最空闲 |
24
| OSPF协议使用(24)报文来保持与其邻居的连接。下面关于OSPF拓扑数据库的描述中,正确的是(25)。 |
| A. Hello |
| B. Keepalive |
| C. SPF |
| D. LSU |
25
| OSPF协议使用(24)报文来保持与其邻居的连接。下面关于OSPF拓扑数据库的描述中,正确的是(25)。 |
| A. 每一个路由器都包含了拓扑数据库的所有选项 |
| B. 在同一区域中的所有路由器包含同样的拓扑数据库 |
| C. 使用Dijkstra算法来生成拓扑数据库 |
| D. 使用LSA分组来更新和维护拓扑数据库 |
26
| TCP协议使用(26)次握手机制建立连接,当请求方发出SYN连接请求后,等待对方回答(27),这样可以防止建立错误的连接。 |
| A. 1 |
| B. 2 |
| C. 3 |
| D. 4 |
27
| TCP协议使用(26)次握手机制建立连接,当请求方发出SYN连接请求后,等待对方回答(27),这样可以防止建立错误的连接。 |
| A. SYN,ACK |
| B. FIN,ACK |
| C. PSH,ACK |
| D. RST,ACK |
28
| 采用DHCP分配IP地址无法做到(28),当客户机发送dhcpdiscover报文时采用(29)方式发送。 |
| A. 合理分配IP地址资源 |
| B. 减少网管员工作量 |
| C. 减少IP地址分配出错可能 |
| D. 提高域名解析速度 |
29
| 采用DHCP分配IP地址无法做到(28),当客户机发送dhcpdiscover报文时采用(29)方式发送。 |
| A. 广播 |
| B. 任意播 |
| C. 组播 |
| D. 单播 |
30
| 客户端登录FTP服务器后使用 (30)命令来上传文件。 |
| A. get |
| B. !dir |
| C. put |
| D. bye |
31
| SMTP传输的邮件报文采用(31)格式表示。 |
| A. ASCII |
| B. ZIP |
| C. PNP |
| D. HTML |
32
| 在下列选项中,属于IIS 6.0提供的服务组件是(32)。 |
| A. Samba |
| B. FTP |
| C. DHCP |
| D. DNS |
33
| 与route print具有相同功能的命令是(33)。 |
| A. ping |
| B. arp -a |
| C. netstat -r |
| D. tracert -d |
34
| 下面的Linux命令中,能关闭系统的命令是(34)。 |
| A. kill |
| B. shutdown |
| C. exit |
| D. logout |
35
| 在Linux中,DNS服务器的配置文件是(35)。 |
| A. /etc/hostname |
| B. /etc/host.conf |
| C. /etc/resolv.conf |
| D. /etc/httpd.conf |
36
| 在Linux中,可以利用(36)命令来终止某个进程。 |
| A. kill |
| B. dead |
| C. quit |
| D. exit |
37
| DNS服务器中提供了多种资源记录,其中(37)定义了区域的邮件服务器及其优先级。 |
| A. SOA |
| B. NS |
| C. PTR |
| D. MX |
38
某用户正在Internet浏览网页,在Windows命令窗口中输入(38)命令后得到下图所示的结果。 若采用抓包器抓获某一报文的以太帧如下图所示,该报文是(39)。 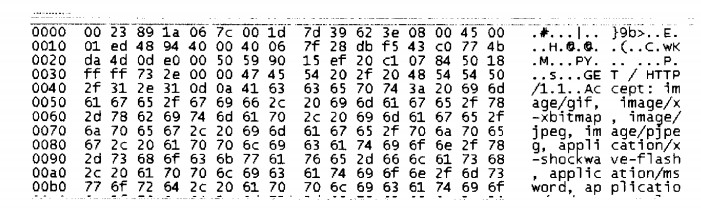 |
| A. arp -a |
| B. ipconfig /all |
| C. route |
| D. nslookup |
39
某用户正在Internet浏览网页,在Windows命令窗口中输入(38)命令后得到下图所示的结果。 若采用抓包器抓获某一报文的以太帧如下图所示,该报文是(39)。  |
| A. 由本机发出的Web页面请求报文 |
| B. 由Internet返回的Web响应报文 |
| C. 由本机发出的查找网关MAC地址的ARP报文 |
| D. 由Internet返回的ARP响应报文 |
40
| 在Windows系统中,默认权限最低的用户组是(40)。 |
| A. everyone |
| B. administrators |
| C. power users |
| D. users |
41
| IIS6.0支持的身份验证安全机制有4种验证方法,其中安全级别最高的验证方法是 (41)。 |
| A. 匿名身份验证 |
| B. 集成Windows身份验证 |
| C. 基本身份验证 |
| D. 摘要式身份验证 |
42
| 以下关于钓鱼网站的说法中,错误的是(42)。 |
| A. 钓鱼网站仿冒真实网站的URL地址 |
| B. 钓鱼网站是一种网络游戏 |
| C. 钓鱼网站用于窃取访问者的机密信息 |
| D. 钓鱼网站可以通过Email传播网址 |
43
| 支持安全Web服务的协议是(43)。 |
| A. HTTPS |
| B. WINS |
| C. SOAP |
| D. HTTP |
44
| 甲和乙要进行通信,甲对发送的消息附加了数字签名,乙收到该消息后利用(44) 验证该消息的真实性。 |
| A. 甲的公钥 |
| B. 甲的私钥 |
| C. 乙的公钥 |
| D. 乙的私钥 |
45
| 下列算法中,(45)属于摘要算法。 |
| A. DES |
| B. MD5 |
| C. Diffie-Hellman |
| D. AES |
46
| 网络的可用性是指(46)。 |
| A. 网络通信能力的大小 |
| B. 用户用于网络维修的时间 |
| C. 网络的可靠性 |
| D. 用户可利用网络时间的百分比 |
47
| 网络管理的5大功能域是(47)。 |
| A. 配置管理、故障管理、计费管理、性能管理和安全管理 |
| B. 配置管理、故障管理、计费管理、带宽管理和安全管理 |
| C. 配置管理、故障管理、成本管理、性能管理和安全管理 |
| D. 配置管理、用户管理、计费管理、性能管理和安全管理 |
48
| SNMPv2提供了3种访问管理信息的方法,这3种方法不包括(48)。 |
| A. 管理站向代理发出通信请求 |
| B. 代理向管理站发出通信请求 |
| C. 管理站与管理站之间的通信 |
| D. 代理向管理站发送陷入报文 |
49
| 嗅探器改变了网络接口的工作模式,使得网络接口 (49)。 |
| A. 只能够响应发送给本地的分组 |
| B. 只能够响应本网段的广播分组 |
| C. 能够响应流经网络接口的所有分组 |
| D. 能够响应所有组播信息 |
50
| ICMP协议的功能包括(50),当网络通信出现拥塞时,路由器发出ICMP (51)报文。 |
| A. 传递路由信息 |
| B. 报告通信故障 |
| C. 分配网络地址 |
| D. 管理用户连接 |
51
| ICMP协议的功能包括(50),当网络通信出现拥塞时,路由器发出ICMP (51)报文。 |
| A. 回声请求 |
| B. 掩码请求 |
| C. 源抑制 |
| D. 路由重定向 |
52
| IP地址分为公网地址和私网地址,以下地址中属于私网地址的是(52)。 |
| A. 10.216.33.124 |
| B. 127.0.0.1 |
| C. 172.34.21.15 |
| D. 192.32.146.23 |
53
| 如果子网172.6.32.0/20被划分为子网172.6.32.0/26,则下面的结论中正确的是(53)。 |
| A. 被划分为62个子网 |
| B. 每个子网有64个主机地址 |
| C. 被划分为32个子网 |
| D. 每个子网有62个主机地址 |
54
| 地址192.168.37.192/25 是(54),地址 172.17.17.255/23 是(55)。 |
| A. 网络地址 |
| B. 组播地址 |
| C. 主机地址 |
| D. 定向广播地址 |
55
| 地址192.168.37.192/25 是(54),地址 172.17.17.255/23 是(55)。 |
| A. 网络地址 |
| B. 组播地址 |
| C. 主机地址 |
| D. 定向广播地址 |
56
| 某公司有2000台主机,则必须给它分配(56)个C类网络。为了使该公司的网络地址在路由表中只占一行,给它指定的子网掩码必须是(57)。 |
| A. 2 |
| B.
8 |
| C. 16 |
| D. 24 |
57
| 某公司有2000台主机,则必须给它分配(56)个C类网络。为了使该公司的网络地址在路由表中只占一行,给它指定的子网掩码必须是(57)。 |
| A. 255.192.0.0 |
| B. 255.240.0.0 |
| C. 255.255.240.0 |
| D. 255.255.248.0 |
58
| 以下给出的地址中,属于子网172.112.15.19/28的主机地址是(58)。 |
| A. 172.112.15.17 |
| B. 172.112.15.14 |
| C. 172.112.15.16 |
| D. 172.112.15.31 |
59
| IPv6地址分为3种类型,它们是(59) 。 |
| A. A类地址、B类地址、C类地址 |
| B. 单播地址、组播地址、任意播地址 |
| C. 单播地址、组播地址、广播地址 |
| D. 公共地址、站点地址、接口地址 |
60
| FTP默认的控制连接端口是(60)。 |
| A. 20 |
| B. 21 |
| C. 23 |
| D. 25 |
61
| 路由器命令 “Router(config)# access-list 1 deny 192.168.1.1 ” 的含义是(61)。 |
| A. 不允许源地址为192.168.1.1的分组通过 |
| B. 允许源地址为192.168.1.1的分组通过 |
| C. 不允许目标地址为192.168.1.1的分组通过 |
| D. 允许目标地址为192.168.1.1的分组通过 |
62
| 局域网冲突时槽的计算方法如下。假设tPHY表示工作站的物理层时延,C表示光速,S表示网段长度,tR表示中继器的时延,在局域网最大配置的情况下,冲突时槽等于 (62)。 |
| A. S/0.7C+2tPHY+8tR |
| B. 2S/0.7C+2tPHY+8tR |
| C. 2S/0.7C+tPHY+8tR |
| D. 2S/0.7C+2tPHY+4tR |
63
| 在局域网标准中,100BASE-T规定从收发器到集线器的距离不超过(63)米。 |
| A. 100 |
| B. 185 |
| C. 300 |
| D. 1000 |
64
| IEEE 802.11 在 MAC 层采用了(64)协议。 |
| A. CSMA/CD |
| B. CSMA/CA |
| C. DQDB |
| D. 令牌传递 |
65
| 在无线局域网中,AP的作用是(65)。新标准IEEE 802.11n提供的最高数据速率可达到(66)。 |
| A. 无线接入 |
| B. 用户认证 |
| C. 路由选择 |
| D. 业务管理 |
66
| 在无线局域网中,AP的作用是(65)。新标准IEEE 802.11n提供的最高数据速率可达到(66)。 |
| A. 54Mb/s |
| B. 100Mb/s |
| C. 200Mb/s |
| D. 300Mb/s |
67
| IEEE 802.16工作组提出的无线接入系统空中接口标准是(67)。 |
| A. GPRS |
| B. UMB |
| C. LTE |
| D. WiMAX |
68
| 安全电子邮件使用(68)协议。 |
| A. PGP |
| B. HTTPS |
| C. MIME |
| D. DES |
69
| 建筑物综合布线系统中的园区子系统是指(69)。 |
| A. 由终端到信息插座之间的连线系统 |
| B. 楼层接线间到工作区的线缆系统 |
| C. 各楼层设备之间的互连系统 |
| D. 连接各个建筑物的通信系统 |
70
| 下面有关RMON的论述中,错误的是(70)。 |
| A. RMON的管理信息库提供整个子网的管理信息 |
| B. RMON的管理信息库属于MIB-2的一部分 |
| C. RMON监视器可以对每个分组进行统计和分析 |
| D. RMON监视器不包含MIB-2的功能 |
71
| The TCP protocol is a (71) layer protocol. Each connection connects two TCPs that may be just one physical network apart or located on opposite sides of the globe. In other words, each connection creates a (72) with a length that may be totally different from another path created by another connection. This means that TCP cannot use the same retransmission time for all connections. Selecting a fixed retransmission time for all connections can result in serious consequences. If the retransmission time does not allow enough time for a (73) to reach the destination and an acknowledgment to reach the source, it can result in retransmission of segment that are still on the way. Conversely, if the retransmission time is longer than necessary for a short path, it may result in delay for the application programs. Even for one single connection, the retransmission time should not be fixed. A connection may be able to send segments and receive (74) faster during nontraffic period than during congested periods. TCP uses the dynamic retransmission time, a transmission time is different for each connection and which may be changed during the same connection. Retransmission time can be made (75) by basing it on the round-trip time (RTT). Several formulas are used for this purpose. |
| A. physical |
| B. network |
| C. transport |
| D. application |
72
| The TCP protocol is a (71) layer protocol. Each connection connects two TCPs that may be just one physical network apart or located on opposite sides of the globe. In other words, each connection creates a (72) with a length that may be totally different from another path created by another connection. This means that TCP cannot use the same retransmission time for all connections. Selecting a fixed retransmission time for all connections can result in serious consequences. If the retransmission time does not allow enough time for a (73) to reach the destination and an acknowledgment to reach the source, it can result in retransmission of segment that are still on the way. Conversely, if the retransmission time is longer than necessary for a short path, it may result in delay for the application programs. Even for one single connection, the retransmission time should not be fixed. A connection may be able to send segments and receive (74) faster during nontraffic period than during congested periods. TCP uses the dynamic retransmission time, a transmission time is different for each connection and which may be changed during the same connection. Retransmission time can be made (75) by basing it on the round-trip time (RTT). Several formulas are used for this purpose. |
| A. path |
| B. window |
| C. response |
| D. process |
73
| The TCP protocol is a (71) layer protocol. Each connection connects two TCPs that may be just one physical network apart or located on opposite sides of the globe. In other words, each connection creates a (72) with a length that may be totally different from another path created by another connection. This means that TCP cannot use the same retransmission time for all connections. Selecting a fixed retransmission time for all connections can result in serious consequences. If the retransmission time does not allow enough time for a (73) to reach the destination and an acknowledgment to reach the source, it can result in retransmission of segment that are still on the way. Conversely, if the retransmission time is longer than necessary for a short path, it may result in delay for the application programs. Even for one single connection, the retransmission time should not be fixed. A connection may be able to send segments and receive (74) faster during nontraffic period than during congested periods. TCP uses the dynamic retransmission time, a transmission time is different for each connection and which may be changed during the same connection. Retransmission time can be made (75) by basing it on the round-trip time (RTT). Several formulas are used for this purpose. |
| A. process |
| B. segment |
| C. program |
| D. user |
74
| The TCP protocol is a (71) layer protocol. Each connection connects two TCPs that may be just one physical network apart or located on opposite sides of the globe. In other words, each connection creates a (72) with a length that may be totally different from another path created by another connection. This means that TCP cannot use the same retransmission time for all connections. Selecting a fixed retransmission time for all connections can result in serious consequences. If the retransmission time does not allow enough time for a (73) to reach the destination and an acknowledgment to reach the source, it can result in retransmission of segment that are still on the way. Conversely, if the retransmission time is longer than necessary for a short path, it may result in delay for the application programs. Even for one single connection, the retransmission time should not be fixed. A connection may be able to send segments and receive (74) faster during nontraffic period than during congested periods. TCP uses the dynamic retransmission time, a transmission time is different for each connection and which may be changed during the same connection. Retransmission time can be made (75) by basing it on the round-trip time (RTT). Several formulas are used for this purpose. |
| A. connections |
| B. requests |
| C. acknowledgents |
| D. datagrams |
75
| The TCP protocol is a (71) layer protocol. Each connection connects two TCPs that may be just one physical network apart or located on opposite sides of the globe. In other words, each connection creates a (72) with a length that may be totally different from another path created by another connection. This means that TCP cannot use the same retransmission time for all connections. Selecting a fixed retransmission time for all connections can result in serious consequences. If the retransmission time does not allow enough time for a (73) to reach the destination and an acknowledgment to reach the source, it can result in retransmission of segment that are still on the way. Conversely, if the retransmission time is longer than necessary for a short path, it may result in delay for the application programs. Even for one single connection, the retransmission time should not be fixed. A connection may be able to send segments and receive (74) faster during nontraffic period than during congested periods. TCP uses the dynamic retransmission time, a transmission time is different for each connection and which may be changed during the same connection. Retransmission time can be made (75) by basing it on the round-trip time (RTT). Several formulas are used for this purpose. |
| A. error |
| B. short |
| C. fixed |
| D. dynamic |
,