1
| 以下关于信息和数据的描述中,错误的是( )。 |
| A. 通常从数据中可以提取信息 |
| B. 信息和数据都由数字组成 |
| C. 信息是抽象的、数据是具体的 |
| D. 客观事物中都蕴涵着信息 |
2
| ( )服务的主要作用是提供远程登录服务。 |
| A. Gopher |
| B. FTP |
| C. Telnet |
| D. E-mail |
3
| 计算机系统中,CPU对主存的访问方式属于( )。 |
| A. 随机存取 |
| B. 顺序存取 |
| C. 索引存取 |
| D. 哈希存取 |
4
| 在指令系统的各种寻址方式中,获取操作数最快的方式是( )。 |
| A. 直接寻址 |
| B. 间接寻址 |
| C. 立即寻址 |
| D. 寄存器寻址 |
5
| 在计算机外部设备和主存之间直接传送而不是由CPU执行程序指令进行数据传送的控制方式称为( )。 |
| A. 程序查询方式 |
| B. 中断方式 |
| C. 并行控制方式 |
| D. DMA方式 |
6
| 若计算机中地址总线的宽度为24位,则最多允许直接访问主存储器( )的物理空间(以字节为单位编址)。 |
| A. 8MB |
| B. 16MB |
| C. 8GB |
| D. 16GB |
7
| 根据《计算机软件保护条例》的规定,著作权法保护的计算机软件是指( )。 |
| A. 程序及其相关文档 |
| B. 处理过程及开发平台 |
| C. 开发软件所用的算法 |
| D. 开发软件所用的操作方法 |
8
| 以下说法中,错误的是( )。 |
| A. 张某和王某合作完成一款软件,他们可以约定申请专利的权利只属于张某 |
| B. 张某和王某共同完成了一项发明创造,在没有约定的情况下,如果张某要对其单独申请专利就必须征得王某的同意 |
| C. 张某临时借调到某软件公司工作,在执行该公司交付的任务的过程中,张某完成的发明创造属于职务发明 |
| D. 甲委托乙开发了一款软件,在没有约定的情况下,由于甲提供了全部的资金和设备,因此该软件著作权属于甲 |
9
| 防火墙对数据包进行过滤时,不能过滤的是( )。 |
| A. 源和目的IP地址 |
| B. 存在安全威胁的URL地址 |
| C. IP协议号 |
| D. 源和目的端口 |
10
| 采用( )表示带符号数据时,算术运算过程中符号位与数值位采用同样的运算规则进行处理。 |
| A. 补码 |
| B. 原码 |
| C. 反码 |
| D. 海明码 |
11
| 与X⊕Y(即X与Y不相同时,X⊕Y的结果为真)等价的逻辑表达式为( )。 |
A.  |
B.  |
C.  |
D.  |
12
| 操作系统的主要任务是( )。 |
| A. 把源程序转换为目标代码 |
| B. 负责文字格式编排和数据计算 |
| C. 负责存取数据库中的各种数据,完成SQL查询 |
| D. 管理计算机系统中的软、硬件资源 |
13
假设某计算机系统中进程的三态模型如下图所示,那么图中的a、b、c、d处应分别填写( )。 |
| A. 作业调度、时间片到、等待某事件、等待某事件发生了 |
| B. 进程调度、时间片到、等待某事件、等待某事件发生了 |
| C. 作业调度、等待某事件、等待某事件发生了、时间片到 |
| D. 进程调度、等待某事件、等待某事件发生了、时间片到 |
14
| 假设系统有n(n≥6)个并发进程共享资源R,且资源R的可用数为3。若采用PV操作,则相应的信号量S的取值范围应为( )。 |
| A. -(n-3)~3 |
| B. -6~3 |
| C. -(n-1)~1 |
| D. -1~n-1 |
15
| 若一个单处理器的计算机系统中同时存在3个并发进程,则同一时刻允许占用处理器的进程数( )。 |
| A. 至少为1个 |
| B. 至少为2个 |
| C. 最多为1个 |
| D. 最多为2个 |
16
| 某计算机系统采用页式存储管理方案,假设其地址长度为32位,其中页号占20位,页内地址占12位。系统中页面总数与页面大小分别为( )。 |
| A. 1K,1024K |
| B. 4K,1024K |
| C. 1M,1K |
| D. 1M, 4K |
17
某算术表达式用二叉树表示如下,该算术表达式的中缀式为(17),其后缀式为(18)。 |
| A. a-b+c*d |
| B. a-(b+c)*d |
| C. (a-(b+c))*d |
| D. a-(b+c*d) |
18
某算术表达式用二叉树表示如下,该算术表达式的中缀式为(17),其后缀式为(18)。 |
| A. abc+-d* |
| B. abcd*+- |
| C. ab-c+d* |
| D. abcd+*- |
19
调用函数时若是引用调用方式,则是将(19)。下面所定义的函数f1为值调用方式,函数f2为引用调用方式。若有表达式x=f1(5),则函数调用执行完成后,该表达式中x获得的值为(20)。 |
| A. 实参的值传给形参 |
| B. 形参的值传给实参 |
| C. 实参的地址传给形参 |
| D. 形参的地址传给实参 |
20
调用函数时若是引用调用方式,则是将(19)。下面所定义的函数f1为值调用方式,函数f2为引用调用方式。若有表达式x=f1(5),则函数调用执行完成后,该表达式中x获得的值为(20)。 |
| A. 5 |
| B. 20 |
| C. 36 |
| D. 45 |
21
| 设数组a[1..10,1..8]中的元素按行存放,每个元素占用4个存储单元,已知第一个数组元素a[1,1]的地址为1004,那么a[5,6]的地址为( )。 |
| A. 1004+(5*8+6)*4 |
| B. 1004+(4*8+5)*4 |
| C. 1004+(5*10+6)*4 |
| D. 1004+(4*10+5)*4 |
22
| 可利用一个栈来检查表达式中的括号是否匹配,其方法是:初始时设置栈为空, 然后从左到右扫描表达式,遇到左括号“(”就将其入栈,遇到右括号“)”就执行出栈操作,忽略其他符号。对于算术表达式“a*(b+c))d”,由于( ),因此可判断出该表达式中的括号不匹配。 |
| A. 需要进行出栈操作但栈已空 |
| B. 需要进行入栈操作但栈已满 |
| C. 表达式处理已结束,但栈中仍留有字符“(” |
| D. 表达式处理已结束,但栈中仍留有字符“)” |
23
| 若有字符串“software”,则其长度为3的子串有( )个。 |
| A. 5 |
| B. 6 |
| C. 7 |
| D. 8 |
24
对下图所示的二叉树进行顺序存储(根结点编号为1,对于编号为i的结点,其左孩子结点为2i,右孩子结点为2i+1)并用一维数组BT来表示,已知结点X、E和D在数组BT中的下标分别为1、2、3, 可推出结点G、K和H在数组BT中的下分别为( )。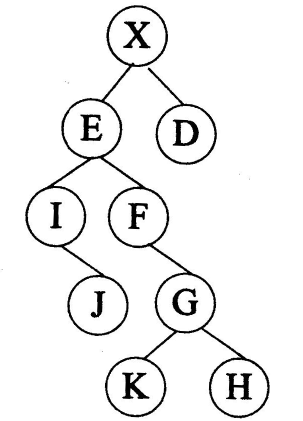 |
| A. 10、11、12 |
| B. 12、24、25 |
| C. 11、12、13 |
| D. 11、22、23 |
25
| 对于关键字序列(10,34,37,51,14,25,56,22,3), 用线性探查法解决冲突构造哈希表,哈希函数为H(key)=key%11,关键字25存入的哈希地址编号为( )。 |
| A. 2 |
| B. 3 |
| C. 5 |
| D. 6 |
26
| 通过设置基准(枢轴)元素将待排序的序列划分为两个子序列,使得其一个子序列的元素均不大于基准元素,另一个子序列的元素均不小于基准元素,然后再分别对两个子序列继续递归地进行相同思路的排序处理,这种排序方法称为( )。 |
| A. 快速排序 |
| B. 冒泡排序 |
| C. 简单选择排序 |
| D. 归并排序 |
27
| 某汽车维修公司有部门、员工和顾客等实体,各实体对应的关系模式如下: 部门(部门代码,部门名称,电话) 员工(员工代码,姓名,部门代码) 顾客(顾客号,姓名,年龄,性别) 维修(顾客号,故障情况,维修日期,员工代码) 假设每个部门允许有多部电话,则电话属性为(27)。若每个部门有多名员工,而每个员工只属于一个部门。员工代码唯一标识员工关系的每一个元组。部门和员工之间是(28)联系。一个员工同一天可为多位顾客维修车辆,而一名顾客,也可由多个员工为其维修车辆,维修关系模式的主键是(29),员工关系模式的外键是(30)。 |
| A. 组合属性 |
| B. 派生属性 |
| C. 多值属性 |
| D. 单值属性 |
28
| 某汽车维修公司有部门、员工和顾客等实体,各实体对应的关系模式如下: 部门(部门代码,部门名称,电话) 员工(员工代码,姓名,部门代码) 顾客(顾客号,姓名,年龄,性别) 维修(顾客号,故障情况,维修日期,员工代码) 假设每个部门允许有多部电话,则电话属性为(27)。若每个部门有多名员工,而每个员工只属于一个部门。员工代码唯一标识员工关系的每一个元组。部门和员工之间是(28)联系。一个员工同一天可为多位顾客维修车辆,而一名顾客,也可由多个员工为其维修车辆,维修关系模式的主键是(29),员工关系模式的外键是(30)。 |
| A. 1:1 |
| B. 1:n |
| C. n:1 |
| D. n:m |
29
| 某汽车维修公司有部门、员工和顾客等实体,各实体对应的关系模式如下: 部门(部门代码,部门名称,电话) 员工(员工代码,姓名,部门代码) 顾客(顾客号,姓名,年龄,性别) 维修(顾客号,故障情况,维修日期,员工代码) 假设每个部门允许有多部电话,则电话属性为(27)。若每个部门有多名员工,而每个员工只属于一个部门。员工代码唯一标识员工关系的每一个元组。部门和员工之间是(28)联系。一个员工同一天可为多位顾客维修车辆,而一名顾客,也可由多个员工为其维修车辆,维修关系模式的主键是(29),员工关系模式的外键是(30)。 |
| A. 顾客号,姓名 |
| B. 顾客号,故障情况 |
| C. 顾客号,维修日期,员工代码 |
| D. 故障情况,维修日期,员工代码 |
30
| 某汽车维修公司有部门、员工和顾客等实体,各实体对应的关系模式如下: 部门(部门代码,部门名称,电话) 员工(员工代码,姓名,部门代码) 顾客(顾客号,姓名,年龄,性别) 维修(顾客号,故障情况,维修日期,员工代码) 假设每个部门允许有多部电话,则电话属性为(27)。若每个部门有多名员工,而每个员工只属于一个部门。员工代码唯一标识员工关系的每一个元组。部门和员工之间是(28)联系。一个员工同一天可为多位顾客维修车辆,而一名顾客,也可由多个员工为其维修车辆,维修关系模式的主键是(29),员工关系模式的外键是(30)。 |
| A. 顾客号 |
| B. 员工代码 |
| C. 维修日期 |
| D. 部门代码 |
31
| 以下关于极限编程(XP)的叙述中,正确的是(31)。XP的12个最佳实践,不包括(32)。 |
| A. XP是激发开发人员创造性、使管理负担最小的一组技术 |
| B. 每一个不同的项目都需要一套不同的策略、约定和方法论 |
| C. 多个自组织和自治小组并行地递增实现产品 |
| D. 有一个使命作为指导,它设立了项目的目标,但并不描述如何达到这个目标 |
32
| 以下关于极限编程(XP)的叙述中,正确的是(31)。XP的12个最佳实践,不包括(32)。 |
| A. 重构 |
| B. 结对编程 |
| C. 精心设计 |
| D. 隐喻 |
33
某软件项目的活动图如下图所示,其中顶点表示项目里程碑,连接顶点的边表示包含的活动,边上的数字表示活动的持续时间(天),则完成该项目的最少时间为(33)天。活动FG的松弛时间为(34)天。 |
| A. 20 |
| B. 30 |
| C. 36 |
| D. 37 |
34
某软件项目的活动图如下图所示,其中顶点表示项目里程碑,连接顶点的边表示包含的活动,边上的数字表示活动的持续时间(天),则完成该项目的最少时间为(33)天。活动FG的松弛时间为(34)天。 |
| A. 1 |
| B. 8 |
| C. 9 |
| D. 17 |
35
| 以下关于软件项目工作量估算的叙述中,不正确的是( )。 |
| A. 专家估计方法受到专家的背景知识和经验的影响 |
| B. 复杂的模型不一定更准确 |
| C. 机器学习方法可以准确估算项目工作量 |
| D. .多种方法结合可以在某种程度上提高估算精度 |
36
| 结构化分析的输出不包括( )。 |
| A. 数据流图 |
| B. 数据字典 |
| C. 加工逻辑 |
| D. 结构图 |
37
| 以下关于数据流图的叙述中,不正确的是( )。 |
| A. 分层数据流图可以清晰地对稍微复杂一些的实际问题建模 |
| B. 用来描述数据流从输入到输出的变换流程 |
| C. 能清晰地表达加工的处理过程 |
| D. 不能表示实体之间的关系 |
38
| 软件设计一般包括概要设计和详细设计,其中概要设计不包括( )。 |
| A. 体系结构设计 |
| B. 模块划分 |
| C. 数据结构设计 |
| D. 模块之间的接口设计 |
39
| MVC模式(模型-视图-控制器)是软件工程中的一种软件架构模式,把软件系统分为模型、视图和控制器三个部分。( )不属于MVC模式的优点。 |
| A. 低耦合性 |
| B. 高重用性 |
| C. 可维护性 |
| D. 高运行效率 |
40
| 某系统中有一个中央数据存储,模块A负责接收新来的数据并修改中央数据存储中的数据,模块B负责访问中央数据存储中的数据则这两个模块之间的耦合类型为(40)。若将这两个模块及中央数据合并成一个模块,则该模块的内聚类型为(41)。 |
| A. 数据 |
| B. 标记 |
| C. 控制 |
| D. 公共 |
41
| 某系统中有一个中央数据存储,模块A负责接收新来的数据并修改中央数据存储中的数据,模块B负责访问中央数据存储中的数据则这两个模块之间的耦合类型为(40)。若将这两个模块及中央数据合并成一个模块,则该模块的内聚类型为(41)。 |
| A. 逻辑 |
| B. 时间 |
| C. 通信 |
| D. 功能 |
42
| 系统交付后,修改偶尔会出现乱码的问题,该行为属于( )维护。 |
| A. 正确性 |
| B. 适应性 |
| C. 完善性 |
| D. 预防性 |
43
| 堆是一种数据结构,分为大顶堆和小顶堆两种类型。大(小)顶堆要求父元素大于等于(小于等于)其左右孩子元素。则(43)是一个小顶堆结构。堆结构用二叉树表示,则适宜的二叉树类型为(44)。对于10个结点的小顶堆,其对应的二叉树的高度(层数)为(45)。堆排序是一种基于堆结构的排序算法,该算法的时间复杂度为(46)。 |
| A. 10,20,50,25,30,55,60,28,32,38 |
| B. 10,20,50,25,38,55,60,28,32,30 |
| C. 60,55,50,38,32,30,28,25,20,10 |
| D. 10,20,60,25,30,55,50,28,32,38 |
44
| 堆是一种数据结构,分为大顶堆和小顶堆两种类型。大(小)顶堆要求父元素大于等于(小于等于)其左右孩子元素。则(43)是一个小顶堆结构。堆结构用二叉树表示,则适宜的二叉树类型为(44)。对于10个结点的小顶堆,其对应的二叉树的高度(层数)为(45)。堆排序是一种基于堆结构的排序算法,该算法的时间复杂度为(46)。 |
| A. 普通二叉树 |
| B. 完全二叉树 |
| C. 二叉排序树 |
| D. 满二叉树 |
45
| 堆是一种数据结构,分为大顶堆和小顶堆两种类型。大(小)顶堆要求父元素大于等于(小于等于)其左右孩子元素。则(43)是一个小顶堆结构。堆结构用二叉树表示,则适宜的二叉树类型为(44)。对于10个结点的小顶堆,其对应的二叉树的高度(层数)为(45)。堆排序是一种基于堆结构的排序算法,该算法的时间复杂度为(46)。 |
| A. 3 |
| B. 4 |
| C. 5 |
| D. 6 |
46
| 堆是一种数据结构,分为大顶堆和小顶堆两种类型。大(小)顶堆要求父元素大于等于(小于等于)其左右孩子元素。则(43)是一个小顶堆结构。堆结构用二叉树表示,则适宜的二叉树类型为(44)。对于10个结点的小顶堆,其对应的二叉树的高度(层数)为(45)。堆排序是一种基于堆结构的排序算法,该算法的时间复杂度为(46)。 |
| A. lgn |
| B. nlgn |
| C. n |
| D. n2 |
47
下图是(47)设计模式的类图,该设计模式的目的是(48),图中,Decorator和Component之间是(49)关系, ConcreteDecorator和Decorator之间是(50)关系。 |
| A. 适配器 |
| B. 桥接 |
| C. 装饰 |
| D. 代理 |
48
下图是(47)设计模式的类图,该设计模式的目的是(48),图中,Decorator和Component之间是(49)关系, ConcreteDecorator和Decorator之间是(50)关系。 |
| A. 将一个类的接口转换为客户期望的另一种接口,使得原本因接口不匹配而无法合作的类可以一起工作 |
| B. 将一个抽象与其实现分离开,以便两者能够各自独立地演变 |
| C. 为一个对象提供代理以控制该对象的访问 |
| D. 动态地给一个对象附加额外的职责,不必通过子类就能灵活地增加功能 |
49
下图是(47)设计模式的类图,该设计模式的目的是(48),图中,Decorator和Component之间是(49)关系, ConcreteDecorator和Decorator之间是(50)关系。 |
| A. 依赖和关联 |
| B. 依赖和继承 |
| C. 关联和实现 |
| D. 继承和实现 |
50
下图是(47)设计模式的类图,该设计模式的目的是(48),图中,Decorator和Component之间是(49)关系, ConcreteDecorator和Decorator之间是(50)关系。 |
| A. 依赖 |
| B. 关联 |
| C. 继承 |
| D. 组合 |
51
| 软件测试的对象不包括( )。 |
| A. 代码 |
| B. 软件测试文档 |
| C. 相关文件数据 |
| D. 开发人员 |
52
| 集成测试的集成方式不包括( )。 |
| A. 一次性集成 |
| B. 自中间到两端集成 |
| C. 自顶向下集成 |
| D. 自底向上集成 |
53
| 以下测试项目不适合采用自动化测试的是( )。 |
| A. 负载压力测试 |
| B. 需要反复进行的测试 |
| C. 易用性测试 |
| D. 可以录制回放的测试 |
54
| 以下关于软件测试目的的叙述中,不正确的是( )。 |
| A. 测试是程序的执行过程,目的在于发现错误 |
| B. 一个好的测试用例在于能发现至今未发现的错误 |
| C. 分析错误产生原因不便于软件过程改进 |
| D. 通过对测试结果分析整理,可以修正软件开发规则 |
55
| 以下关于软件测试分类的叙述中,不正确的是( )。 |
| A. 按照软件开发阶段可分为单元测试、集成测试、系统测试等 |
| B. 按照测试实施组织可分为开发方测试、用户测试和第三方测试等 |
| C. 按照测试技术可分为白盒测试、黑盒测试等 |
| D. 按照测试持续时长可分为确认测试、验收测试等 |
56
| 以下关于软件质量属性的叙述中,不正确的是( )。 |
| A. 功能性是指软件满足明确和隐含要求功能的能力 |
| B. 易用性是指软件能被理解、学习、使用和吸引用户的能力 |
| C. 效率是指软件维持规定容量的能力 |
| D. 维护性是指软件可被修改的能力 |
57
| Bug记录信息包括( )。 ①被测软件名称 ②被测软件版本 ③测试人 ④错误等级 ⑤开发人 ⑥详细步骤 |
| A. ①③④⑥ |
| B. ①②④⑥ |
| C. ①②③④⑥ |
| D. ①②③④⑤⑥ |
58
| 自动化测试的优势不包括( )。 |
| A. 提高测试效率 |
| B. 提高测试覆盖率 |
| C. 适用于所有类型的测试 |
| D. 更好地利用资源 |
59
| 以下关于因果图法测试的叙述中,不正确的是( )。 |
| A. 因果图法是从自然语言书写的程序规格说明中找出因和果 |
| B. 因果图法不一定需要把因果图转成判定表 |
| C. 为了去掉不可能出现的因果组合,需要标明约束条件 |
| D. 如果设计阶段就采用了判定表,则不必再画因果图 |
60
| 一个程序的控制流图中有8个节点、12条边,在测试用例数最少的情况下,确保程序中每个可执行语句至少执行一次所需测试用例数的上限是( )。 |
| A. 2 |
| B. 4 |
| C. 6 |
| D. 8 |
61
| 对于逻辑表达式(((a|b)‖(c>2))&&d<0),需要( )个测试用例才能完成条件组合覆盖。 |
| A. 2 |
| B. 4 |
| C.
8 |
| D. 16 |
62
| ( )不属于网络测试对象。 |
| A. 服务器 |
| B. 路由器 |
| C. 网段 |
| D. CPU |
63
| ( )不属于网络测试的测试类型。 |
| A. 可靠性测试 |
| B. 可接受性测试 |
| C. 存储容量测试 |
| D. 吞吐量测试 |
64
| ( )不属于数据库性能测试的测试指标。 |
| A. 内存利用 |
| B. 会话统计 |
| C. 带宽 |
| D. SQL执行情况 |
65
| 以下关于文档测试的叙述中,不正确的是( )。 |
| A. 文档要面向所有级别读者 |
| B. 文档中用到的术语要符合行业规范 |
| C. 需要检查所有信息是否真实正确 |
| D. 需要检查软件返回结果跟文档描述是否一致 |
66
| 以下关于web测试的叙述中,不正确的是( )。 |
| A. 与其它系统的测试内容不同 |
| B. 与其它系统的测试手段基本相同 |
| C. 与其它系统的测试重点不同 |
| D. 与其它系统采用的测试工具部分不同 |
67
| 用户口令测试应考虑的测试点包括( )。 ①口令时效 ②口令长度 ③口令复杂度 ④口令锁定 |
| A. ①③ |
| B. ②③ |
| C. ①②③ |
| D. ①②③④ |
68
| 以下不属于易用性测试的是( )。 |
| A. 安装测试 |
| B. 负载测试 |
| C. 功能易用性测试 |
| D. 界面测试 |
69
| 通过遍历用例的路径上基本流和备选流的黑盒测试方法是( )。 |
| A. 等价类划分法 |
| B. 因果图法 |
| C. 边界值分析法 |
| D. 场景法 |
70
| 以下关于软件质量保证的叙述中,不正确的是( )。 |
| A. 软件质量是指软件满足规定或潜在用户需求的能力 |
| B. 质量保证通过预防、检查与改进来保证软件质量 |
| C. 质量保证关心的是开发过程活动本身 |
| D. 质量保证的工作主要是通过测试找出更多问题 |
71
| The project workbook is not so much a separate document as it is a structure imposed on the documents that the project will be producing anyway. All the documents of the project need to be part of this (71). This includes objectives ,external specifications , interface specifications , technical standards , internal specifications and administrative memoranda(备忘录). Technical prose is almost immortal. If one examines the genealogy ( 手册 ) of a customer manual for a piece of hardware or software , one can trace not only the ideas , but also many of the very sentences and paragraphs back to the first (72) proposing the product or explaining the first design. For the technical writer, the paste-pot is as mighty as the pen. Since this is so, and since tomorrow’s product-quality manuals will grow from today’s memos, it is very important to get the structure of the documentation right. The early design of the project (73) ensures that the documentation structure itself is crafted, not haphazard. Moreover, the establishment of a structure molds later writing into segments that fit into that structure. The second reason for the project workbook is control of the distribution of (74). The problem is not to restrict information, but to ensure that relevant information gets to all the people who need it. The first step is to number all memoranda, so that ordered lists of titles are available and h worker can see if he has what he wants. The organization of the workbook goes well beyond this to establish a tree-structure of memoranda. The (75) allows distribution lists to be maintained by subtree, if that is desirable. |
| A. structure |
| B. specification |
| C. standard |
| D. objective |
72
| The project workbook is not so much a separate document as it is a structure imposed on the documents that the project will be producing anyway. All the documents of the project need to be part of this (71). This includes objectives ,external specifications , interface specifications , technical standards , internal specifications and administrative memoranda(备忘录). Technical prose is almost immortal. If one examines the genealogy ( 手册 ) of a customer manual for a piece of hardware or software , one can trace not only the ideas , but also many of the very sentences and paragraphs back to the first (72) proposing the product or explaining the first design. For the technical writer, the paste-pot is as mighty as the pen. Since this is so, and since tomorrow’s product-quality manuals will grow from today’s memos, it is very important to get the structure of the documentation right. The early design of the project (73) ensures that the documentation structure itself is crafted, not haphazard. Moreover, the establishment of a structure molds later writing into segments that fit into that structure. The second reason for the project workbook is control of the distribution of (74). The problem is not to restrict information, but to ensure that relevant information gets to all the people who need it. The first step is to number all memoranda, so that ordered lists of titles are available and h worker can see if he has what he wants. The organization of the workbook goes well beyond this to establish a tree-structure of memoranda. The (75) allows distribution lists to be maintained by subtree, if that is desirable. |
| A. objective |
| B. memoranda |
| C. standard |
| D. specification |
73
| The project workbook is not so much a separate document as it is a structure imposed on the documents that the project will be producing anyway. All the documents of the project need to be part of this (71). This includes objectives ,external specifications , interface specifications , technical standards , internal specifications and administrative memoranda(备忘录). Technical prose is almost immortal. If one examines the genealogy ( 手册 ) of a customer manual for a piece of hardware or software , one can trace not only the ideas , but also many of the very sentences and paragraphs back to the first (72) proposing the product or explaining the first design. For the technical writer, the paste-pot is as mighty as the pen. Since this is so, and since tomorrow’s product-quality manuals will grow from today’s memos, it is very important to get the structure of the documentation right. The early design of the project (73) ensures that the documentation structure itself is crafted, not haphazard. Moreover, the establishment of a structure molds later writing into segments that fit into that structure. The second reason for the project workbook is control of the distribution of (74). The problem is not to restrict information, but to ensure that relevant information gets to all the people who need it. The first step is to number all memoranda, so that ordered lists of titles are available and h worker can see if he has what he wants. The organization of the workbook goes well beyond this to establish a tree-structure of memoranda. The (75) allows distribution lists to be maintained by subtree, if that is desirable. |
| A. title |
| B. list |
| C. workbook |
| D. quality |
74
| The project workbook is not so much a separate document as it is a structure imposed on the documents that the project will be producing anyway. All the documents of the project need to be part of this (71). This includes objectives ,external specifications , interface specifications , technical standards , internal specifications and administrative memoranda(备忘录). Technical prose is almost immortal. If one examines the genealogy ( 手册 ) of a customer manual for a piece of hardware or software , one can trace not only the ideas , but also many of the very sentences and paragraphs back to the first (72) proposing the product or explaining the first design. For the technical writer, the paste-pot is as mighty as the pen. Since this is so, and since tomorrow’s product-quality manuals will grow from today’s memos, it is very important to get the structure of the documentation right. The early design of the project (73) ensures that the documentation structure itself is crafted, not haphazard. Moreover, the establishment of a structure molds later writing into segments that fit into that structure. The second reason for the project workbook is control of the distribution of (74). The problem is not to restrict information, but to ensure that relevant information gets to all the people who need it. The first step is to number all memoranda, so that ordered lists of titles are available and h worker can see if he has what he wants. The organization of the workbook goes well beyond this to establish a tree-structure of memoranda. The (75) allows distribution lists to be maintained by subtree, if that is desirable. |
| A. product |
| B. manual |
| C. document |
| D. information |
75
| The project workbook is not so much a separate document as it is a structure imposed on the documents that the project will be producing anyway. All the documents of the project need to be part of this (71). This includes objectives ,external specifications , interface specifications , technical standards , internal specifications and administrative memoranda(备忘录). Technical prose is almost immortal. If one examines the genealogy ( 手册 ) of a customer manual for a piece of hardware or software , one can trace not only the ideas , but also many of the very sentences and paragraphs back to the first (72) proposing the product or explaining the first design. For the technical writer, the paste-pot is as mighty as the pen. Since this is so, and since tomorrow’s product-quality manuals will grow from today’s memos, it is very important to get the structure of the documentation right. The early design of the project (73) ensures that the documentation structure itself is crafted, not haphazard. Moreover, the establishment of a structure molds later writing into segments that fit into that structure. The second reason for the project workbook is control of the distribution of (74). The problem is not to restrict information, but to ensure that relevant information gets to all the people who need it. The first step is to number all memoranda, so that ordered lists of titles are available and h worker can see if he has what he wants. The organization of the workbook goes well beyond this to establish a tree-structure of memoranda. The (75) allows distribution lists to be maintained by subtree, if that is desirable. |
| A. list |
| B. document |
| C. tree-structure |
| D. number |
,